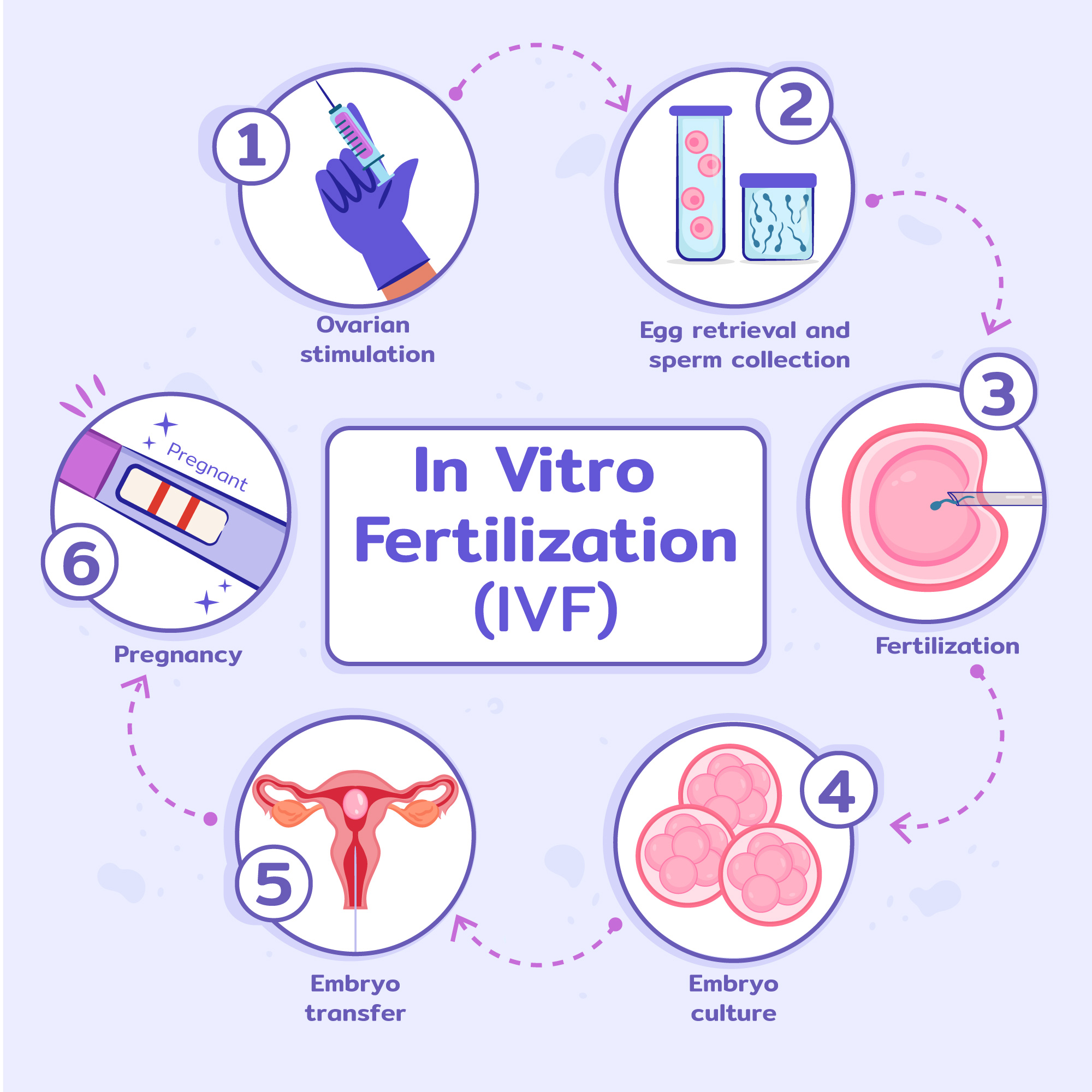
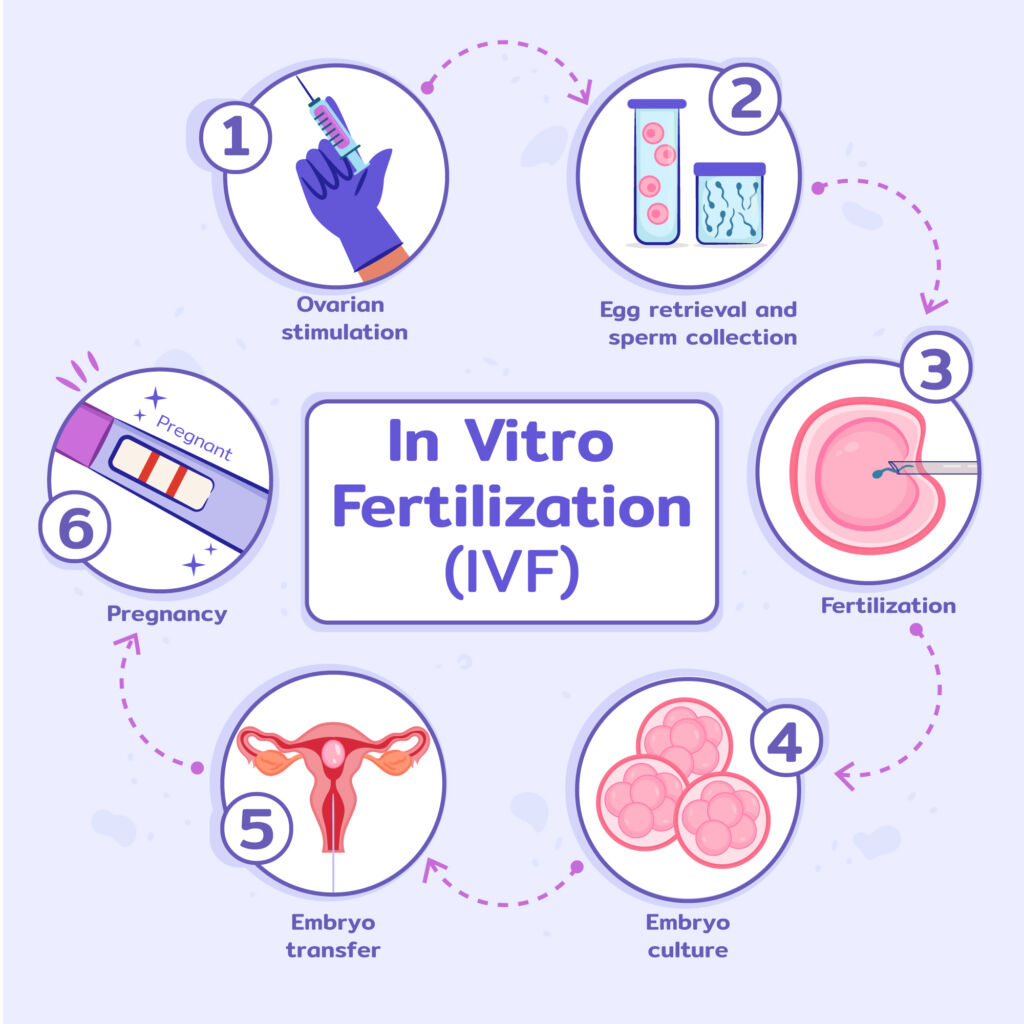
What is IVF? IVF (In Vitro Fertilization)
IVF, or in vitro fertilization, is the miracle of conception, a remarkable breakthrough that helped millions of childless couples welcome their babies.
IVF is a procedure where mature eggs are collected from ovaries and fertilized with sperm outside the body, typically in a petri dish. The term ‘in vitro’ comes from Latin, which literally means in the glass. The fertilized embryo is then placed inside the uterus to develop into a baby.
IVF was first introduced in 1978 and has contributed to the birth of over 10 million babies. The babies born with the help of IVF, often referred as ‘test-tube babies’, are just as normal as those born through natural conception. Opting for IVF is a deeply personal decision, as the process can be quite overwhelming. It is typically recommended for couples experiencing infertility. Infertility is the condition where a couple is not able to naturally conceive a child even after a year long of trying. It is a common conception among people to assume that IVF is a risky and complicated procedure. To dispel these misconceptions and doubts, we have briefly outlined the different steps of the IVF process:
Step-by-step breakdown of IVF
- Preparation
The first procedure that you will be going through in your IVF journey is preparation. This involves undergoing several screening tests to provide the doctor with essential information about the condition of your uterus, the size and quality of your eggs, and the best way to implant the embryo. Some of the screenings include:
Ovarian reserve testing
Imagine the ovary as a vault that releases a number of eggs every month. The number of eggs released will vary from person to person and depend on their health conditions. Blood tests and ultrasounds are performed on the mother to evaluate and determine the condition and number of eggs are in the reserve. The egg supply of your ovary can be determined through these tests, enabling doctors to determine if it will respond to the fertility medicines used later in the process.
Semen analysis
The role of male fertility is critical in achieving conception. The sperm will be collected, and its characteristics, such as count, shape, size, and quality, will be tested. This is the initial fertility evaluation of the sperm. Low sperm count, morphology or normal sperm movement are identified and treatable conditions are then carried out through minor procedures. If the sperm is unfit for fertilization, then the couple can opt for a sperm donor.
Infectious diseases
Both parents will undergo testing for infectious diseases, such as HIV, to ensure that their bodies are in optimal condition for the IVF process. These tests are crucial to safeguarding the health of both the parents and the potential baby.
- Stimulation
Once the doctors determine the count of the eggs and their condition, they start with the process called stimulation. In this process, the mother receives fertility drugs for the egg to grow. These drugs are normally produced by your glands, but now they’re being injected to stimulate and enhance the growth of the eggs.
After the fertility drugs are stimulated, the monitoring visits start. Monitoring will be done through ultrasound and blood tests to measure the follicles, check for estrogen, and make changes accordingly. Since egg maturity can vary from person to person, this monitoring is crucial. It helps doctors determine the optimal time when the eggs are most mature and ready for retrieval.
- Egg retrieval
The egg retrieval process is also known as follicular aspiration. When the eggs are mature, a trigger shot is given to prepare them for retrieval. It is a minimally invasive and low-risk procedure, but it will be done under anesthesia to ensure the mother’s comfort. A surgical needle is used to extract eggs from the ovaries by inserting it through the vaginal side walls.This needle enters each follicle to drain out the follicular fluid. The needle is attached to a small suction to retrieve the eggs. The eggs will then be transferred into a petri dish, identified, and assessed in the lab.
- Insemination
On the same day as the egg retrieval, sperm will be collected and combined with the mature eggs in a petri dish, where fertilization takes place.These are the two most commonly used fertilization methods:
Conventional Fertilization
Conventional fertilization involves placing the sperm and eggs together in a petri dish, incubating them overnight, and then checking to see how many eggs have been fertilized. This method is typically used when there are no significant issues with the sperm or eggs.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is a procedure in which a single sperm is manually injected directly into a mature egg. If the couple is facing fertilization issues, this is the commonly chosen method because it ensures a higher chance of fertilization as it is manually done. ICSI is particularly useful in cases of male infertility, certain diseases, or conditions like PCOS.
For conventional fertilization, there is approximately a 60% chance of fertilization, though it is difficult to predict the exact number of eggs that will fertilize since not all may be mature. In contrast, the ICSI procedure involves removing the outer cells of the egg to confirm its maturity, resulting in a higher fertilization rate of 75 to 80%.
Depending on your situation, IVF can use:
* Your eggs and your partner’s sperm
* Your eggs and donor sperm
* Donor eggs and your partner’s sperm
* Donor eggs and donor sperm
* Donated embryos
Another option is to use the help of a surrogate or gestational carrier. A gestational woman is a woman who carries your baby for you. They will have no genetic connection to the child she carries. Women for whom pregnancy poses significant health risks have the option to choose surrogacy instead.
- Embryo Culture
5 to 6 days are given after fertilization for the egg to grow out to reach the blastocyst stage. The embryo, when fully ready for transfer, will have around 300 cells. It will expand, and the outer wall will be formed. It is called trophectoderm , and this wall will further develop into forming the placenta. The smaller group of cells inside the embryo will grow into the baby.
- Transfer
Once the embryo culture is done, it is now ready to be transferred into the uterus. It is done through a simple procedure where the mother will receive a mild sedative to help them relax firstly . The procedure is usually painless, though you might experience mild cramping. A long, thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted through the vagina, cervix, and into the uterus. A syringe containing one or more embryos in a small amount of fluid is attached to the catheter, and the embryos are then placed into the uterus. If the procedure turns out to be successful, the embryo will attach to the uterus lining around 6-8 days after the egg retrieval.
Genetic testing of the embryo can be performed at this stage before transfer. If the parents have genetic disorders and do not wish to pass them on to their child, they can opt for genetic testing. This ensures that only embryos without these genetic disorders are implanted.
Results
12 days after egg retrieval, blood tests are performed to assess the success of the procedure. If the test confirms pregnancy, the medications are continued as per protocol for the next 12 weeks. After this period, the patient will be referred to an obstetrician for further prenatal care.
If the pregnancy test comes out negative, the medications are discontinued. Menstruation typically resumes within about ten days, after which the patient can consider another IVF cycle or embryo transfer.
Who would require IVF?
Broadly speaking, couples who can’t conceive naturally require the procedure. IVF is the most advanced form of infertility procedure. There are various minor procedures that might be suitable for some cases. Once your monitoring is complete, IVF will be performed only if certain conditions necessitate it. Some health conditions that might require IVF include:
Age:
For women over the age of 35, the chances of fertilization decrease due to a decline in egg quality, ovarian reserve, and the regularity of egg release.The chances of miscarriage is also higher in older women. Women in their 40s face several health risks while trying to conceive, making IVF a viable option to get over these risks and improve the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Fallopian tube damage or blockage:
The fallopian tube is the part of the female reproductive system where fertilization occurs. The fertilized egg needs to travel from the ovary to the uterus through the fallopian tube, so if there is damage or a blockage in the tube, transfer of the fertilized egg will be difficult. But through IVF, the fertilized egg can be directly implanted into the uterus without having to travel through a fallopian tube.
Ovulation disorders:
This is when the ovulation cycle doesn’t occur often or has irregular patterns. It will result in fewer and fewer mature eggs, which decreases the chance of fertility.
Endometriosis:
Endometriosis occurs when tissue resembling the lining of the uterus, which normally prepares to receive a fertilized egg, grows outside the uterus. Endometriosis can affect the ovaries, uterus, and fallopian tubes, which may result in pain and fertility issues. It affects approximately 10 to 15% of women attempting to conceive.
Uterine fibroids:
These fibroids are tumors, but most often they are not cancer. This is commonly found in women in the age of 30, which makes it difficult for the fertilized egg to attach to the lining of the uterus.
Previous surgery to prevent pregnancy:
If the woman has gone through tubal ligation, a process where the fallopian tube is cut or blocked to prevent pregnancy, and later wishes to get pregnant, there is no need to reverse the surgery. IVF can be performed instead, where the fertilized egg is directly placed into the uterus.
Issues with sperm :
Low sperm count, abnormal sperm movement, or issues with sperm size and shape can make fertilization difficult. While there are several treatment options available for these conditions, if the sperm quality is inadequate for fertilization, couples may choose to use a sperm donor instead.
Genetic disorders:
A fertilized egg can undergo genetic screening before implantation. While not all disorders can be detected, it provides insight into the embryo’s genetic health before it is placed in the uterus.
Preserve due to health conditions:
When the couple is battling with health conditions such as cancer, the treatment will involve procedures like chemotherapy or radiology, which will drastically affect the fertilization capability. So if the couple wishes to be parents in the future, they can either freeze their eggs or fertilize their embryos before the procedure. This preserves their ability to become parents in the future, despite the potential effects of medical treatments.
Unexplained infertility:
IVF is a viable option for couples who undergo extensive testing yet cannot pinpoint the cause of their infertility.
General Timeline
Here is the general timeline for the IVF process, although it varies depending on individual health conditions and the specific hospital where the procedure is performed.
Day 1: Menstrual cycle starts
Day 2–4: Ovarian stimulation
Day 5–7: Monitoring
Day 8–10: Trigger Shot
Day 11 to 12: Egg retrieval
Day 13 to 14: Fertilization
Day 15 to 19: Embryo culture
Day 20 to 21 embryo transfer
Date 22–30 Luteal process and pregnancy test
Success rate
The success rate heavily depends on a lot of causative factors, such as:
- Age
- BMI
- Miscarriage history
- Reasons for infertility
- Previous deliveries
Age factor
The age of the mother determines the chance of success in IVF.
Below 30 years: 62% chance
35 years: 55% chance
35 to 40 years: 30 to 45% chance
Above 40: 15% chance
Financial aspect
Being familiar with the cost of IVF treatment is necessary to plan your journey. No two IVF treatments are the same. The procedure varies from person to person, as there are several factors like the patient’s medical conditions, age, and additional procedures and protocols that are unique to every couple. Only after a comprehensive study of the case will doctors be able to determine the total cost of the treatment. At Credence IVF, the cost of IVF treatment comes around 1.2 lakhs, which is subjected to increase or decrease according to the case of the patient. A detailed breakdown of the exact cost will be provided prior to the treatment.
Conclusion
Your path to parenthood and fulfilling the dream of creating a beautiful family does not have to be filled with challenges and stressful times. The hospital you choose for your treatment plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and comfortable journey.
Credence Hospital is Trivandrum’s leading family hospital specializing in the care of women and children. With 20+ years of experience in the field, Credence IVF is a pioneer in reproductive medicine and sets the standard high for infertility and Best IVF Treatment Centre in Kerala
When it comes to your family and the life of your little one, you deserve nothing but the best. So choose Credence IVF, the best infertility hospital in India. With its expert team of doctors, world-class diagnostic, and most advanced infertility treatment facilities,



